WHAT ARE CAN-BUS AND THE J1939 STANDARD IN VANGUARD BATTERIES?
- This FAQ article applies to all Vanguard battery packs -
Content

BUS - the physical wires a CAN system uses (like a main line, loop)
Simply put, CAN-Bus is a kind of ''network'' that allows all devices connected to the bus to ''talk'' to each other. It is a robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other without a host computer. Originally developed by Bosch in the 1980s, it is widely used in automotive and industrial applications.
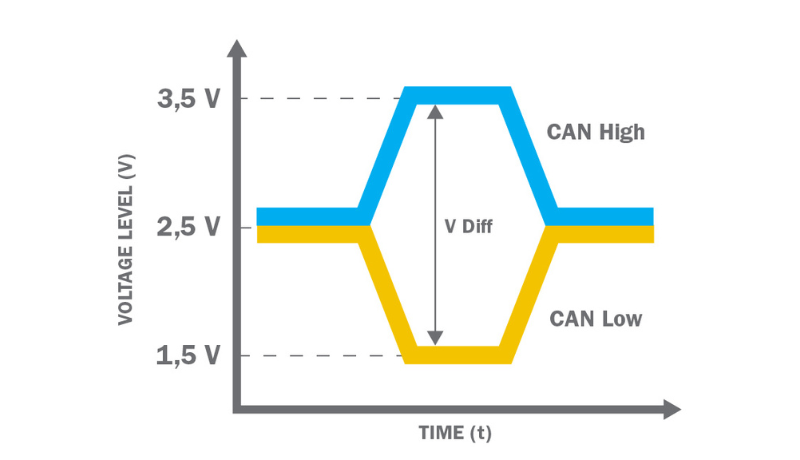
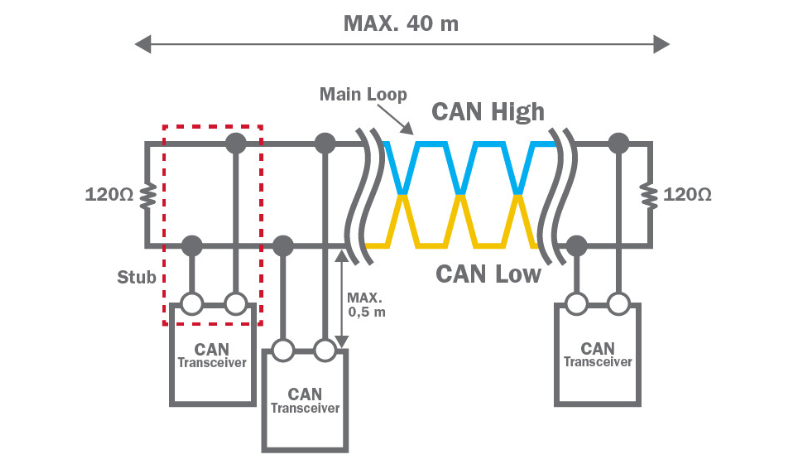
A CAN bus line is constructed using a twisted pair of wires that have a 120-ohm terminating resistor on each end. One wire is designated as CAN High, with the other named CAN Low. All devices connected to the bus are known as electronic control units (ECUs) or nodes.
The BMS mentioned earlier works like a node and can communicate through the CAN protocol with all other devices connected to that network. When using the CAN bus, a single ECU can transmit data to all other ECUs connected to the system. Those ECUs can review the information and choose to receive or ignore it.
In our 48V Vanguard batteries we use the double can-bus communication with 29-Bit J1939 standard with baud rate 500kBps.
Two-Wire System: CAN-Bus uses a two-wire twisted pair for communication. The two wires are known as CAN_H (high) and CAN_L (low).
Multi-Master Protocol: Any node (device) on the network can initiate communication. This means there is no need for a central controller.
Message-Based Protocol: Communication is based on messages rather than direct node-to-node communication. Each message has a unique identifier.
Error Detection: CAN-Bus includes extensive error detection mechanisms and fault confinement, making it reliable even in noisy environments.
Data Transmission: Devices (nodes) connected to the CAN-Bus network send and receive messages. Each message contains an identifier, which signifies the priority of the message and its purpose.
Arbitration: When multiple nodes attempt to send messages simultaneously, the CAN-Bus uses a non-destructive bitwise arbitration method to determine which message has the highest priority and should be sent first.
Error Handling: CAN-Bus continuously monitors for errors. If an error is detected, the message is flagged and retransmitted. Nodes that consistently cause errors are eventually disconnected from the network.
FURTHER BATTERY FAQs
GET SUPPORT
Take advantage of the expertise your local dealer can provide for service and support on your Vanguard engine.
MANUALS & IPLS
Download the operator's manual for your Vanguard engine or equipment by following our step-by-step process.